Before Manual Psoas Release
Understanding the Psoas Muscle Anatomy
The psoas muscle, running from the lower back to the femur, plays a crucial role in hip flexion and spinal stability. Its deep location makes it challenging to access, but its release can significantly ease tension and improve mobility.
The psoas muscle, often referred to as the “so-ezz” muscle, is a long, deep-seated muscle that runs from the lower back (lumbar spine) down to the femur (thigh bone). It plays a vital role in hip flexion, enabling actions like walking, running, and bending. The psoas muscle is part of the iliopsoas muscle group, which also includes the iliacus muscle. Together, they work to stabilize the pelvis and spine, making them essential for maintaining proper posture and movement.
The psoas muscle is unique because it is the only muscle that connects the spine to the leg. It originates from the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) and inserts on the lesser trochanter of the femur. This anatomical arrangement allows it to influence both the lower back and hip joint simultaneously. The muscle also interacts closely with the lumbar plexus, a network of nerves near its origin, which can contribute to referred pain patterns when the muscle is tight or restricted.
Understanding the psoas muscle’s anatomy is crucial for effective manual release. Its deep location, surrounded by other tissues and organs, makes it challenging to target directly. However, its central role in movement and posture means that releasing tension in this muscle can have profound effects on overall physical and emotional well-being.
Identifying Causes of Psoas Tightness
Psoas tightness often arises from a combination of lifestyle, movement patterns, and emotional factors. Prolonged sitting, common in modern life, shortens the psoas muscle, leading to chronic tension. Overuse from activities like running or cycling can also overactivate the psoas, causing tightness. Poor posture, such as an anterior pelvic tilt, further exacerbates the issue by placing constant strain on the muscle.
Stress and emotional tension can contribute to psoas tightness, as the muscle is linked to the body’s “fight or flight” response. When stressed, the psoas may contract and remain tense, creating discomfort. Additionally, muscle imbalances, such as weak abdominal muscles or tight hip flexors, can disrupt the psoas’ function, leading to tightness and restricted movement.
Previous injuries, like lower back strains or hip injuries, may also cause the psoas to become guarded and tight as a protective mechanism. Understanding these causes is essential for addressing psoas tightness effectively and preparing for manual release. By identifying the root factors, individuals can take targeted steps to alleviate tension and improve overall mobility.
Preparing for Manual Psoas Release

Proper preparation is essential for a safe and effective manual psoas release. Begin by creating a comfortable environment, ensuring the surface is firm yet supportive, such as a massage table or a mat on the floor. It’s crucial to warm up the body beforehand with light exercises like gentle stretching or dynamic movements to increase blood flow to the muscle tissue.
Wearing loose, comfortable clothing allows for ease of movement and access to the target area. Hydration is also important, as it helps maintain muscle elasticity and promotes relaxation. Before starting, take a few minutes to practice deep, slow breathing to calm the nervous system and reduce tension. This helps the muscle respond better to the release process.

If using tools like the Pso-Rite or a foam roller, familiarize yourself with their proper use to avoid discomfort or injury. Consulting with a healthcare professional or experienced practitioner is recommended, especially for those new to manual release techniques. They can guide you through the process and ensure you’re prepared both physically and mentally. Proper preparation enhances the effectiveness of the release and minimizes potential discomfort.
What to Expect During the Release
During a manual psoas release, you may experience a range of sensations, from mild discomfort to significant relief. The process typically involves gentle yet firm pressure applied to the muscle, often through specific techniques or tools designed to target the deep-seated tissue. It’s common to feel a deep ache or tension as the muscle begins to relax and release stored stress.
Some individuals report feeling emotional responses, such as tears or sighs, as the release can unlock both physical and emotional tension. This is because the psoas muscle is closely linked to the body’s stress response and can hold onto emotional trauma. The practitioner may guide you through deep breathing exercises to enhance the release and help you stay relaxed.
The duration of the session varies, but most releases take 15–30 minutes. After the process, you might feel a sense of lightness or freedom in your lower back and hips, as well as improved mobility. While the experience can be intense, many find it profoundly relieving, leading to a deeper connection between body and mind.

After Manual Psoas Release
After manual psoas release, individuals often experience immediate physical benefits such as lower back pain relief and improved flexibility. Emotional tension may ease, leading to a sense of relaxation. Posture and mobility typically improve, enhancing overall well-being.
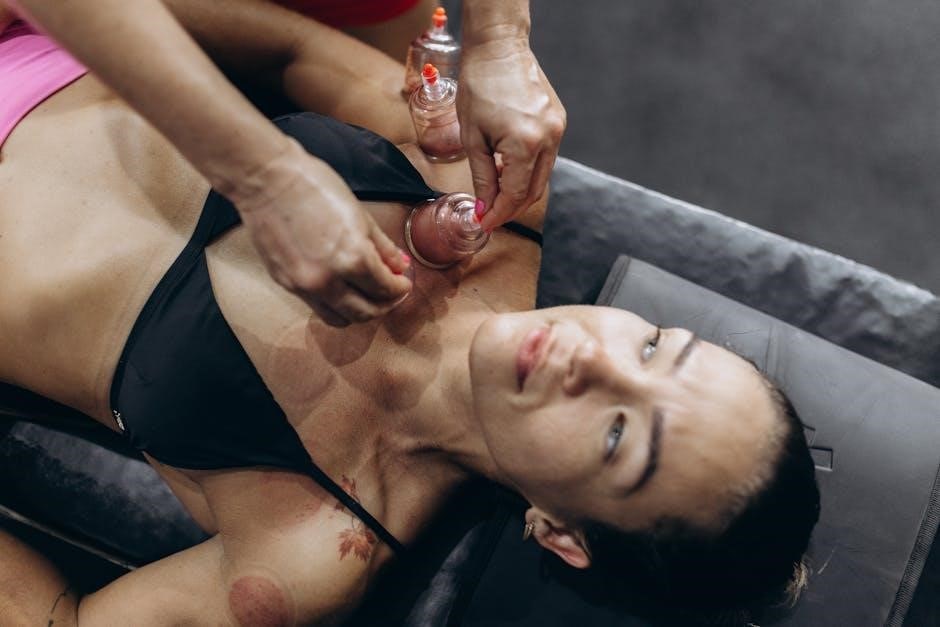

Immediate Physical Benefits
Immediately following a manual psoas release, individuals often report significant physical relief. Lower back pain and hip discomfort frequently diminish, as tension in the psoas muscle is alleviated. Improved flexibility and range of motion are common, allowing for easier movement and a reduction in stiffness.
Breathing often becomes deeper and more relaxed, as the psoas muscle’s release can reduce pressure on the diaphragm. This can enhance overall respiratory function and promote a sense of calm. Additionally, posture may improve instantly, as the muscle’s relaxation allows the spine to align more naturally.

Many people experience a noticeable reduction in muscle spasms and tightness, particularly in the lower back and hips. The release can also improve circulation, as relaxed muscles allow blood to flow more freely, further aiding in pain relief and muscle recovery.
- Reduced lower back and hip pain
- Enhanced flexibility and mobility
- Improved breathing and relaxation
- Better spinal alignment and posture
- Reduced muscle spasms and stiffness
These immediate physical benefits highlight the profound impact of manual psoas release on both comfort and function, making it a valuable therapy for many individuals.
Emotional and Psychological Changes
Manual psoas release often triggers profound emotional and psychological shifts. The psoas muscle is deeply connected to the body’s “fight or flight” response, and its relaxation can calm the sympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and anxiety.
Many individuals report feeling a sense of emotional release, such as crying or sighing deeply, as stored tension is freed. This release can lead to heightened emotional awareness and a greater sense of calm. The connection between the psoas and the body’s emotional center can also foster a deeper sense of grounding and stability.
The psychological benefits often include improved mental clarity and reduced feelings of overwhelm. By addressing physical tension, manual psoas release can create a ripple effect, positively impacting emotional resilience and overall well-being. While experiences vary, many find the process profoundly therapeutic, bridging the gap between physical relief and emotional healing.
Improvements in Posture and Mobility

Manual psoas release can lead to significant improvements in posture and mobility. By relieving tension in the psoas muscle, the body naturally adopts a more upright and balanced alignment, reducing the strain on the lower back and hips.

Individuals often notice enhanced flexibility in the hip joint, making movements like walking, climbing stairs, and bending easier and less painful. The release of chronic tightness allows for a fuller range of motion, restoring the body’s natural movement patterns.
Improved posture not only enhances physical appearance but also supports better breathing and spinal health. Over time, consistent psoas maintenance can prevent the return of restrictive patterns, fostering long-term mobility and reducing the risk of recurring discomfort.
Overall, the combination of reduced tension and restored alignment creates a foundation for more fluid, effortless movement, enabling individuals to engage in daily activities with greater ease and confidence.
Maintaining Psoas Health
Maintaining psoas health is essential to prevent recurring tightness and promote long-term well-being. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises, such as gentle yoga poses or targeted stretches, can help keep the psoas muscle flexible and balanced.

Incorporating activities like swimming or walking can also support psoas health by encouraging natural movement patterns without overtaxing the muscle. Using tools like the Pso-Rite or QL Claw for self-release can be an effective way to maintain relaxation and prevent tension buildup.
Additionally, adopting good posture and avoiding prolonged sitting can significantly reduce strain on the psoas. Engaging in regular manual therapy sessions with a licensed practitioner can further ensure the muscle remains healthy and functioning optimally.
By combining these practices, individuals can enjoy sustained relief from psoas-related discomfort and maintain improved mobility and posture over time.
Long-Term Well-Being
Manual psoas release can lead to significant long-term improvements in overall well-being. By addressing chronic tightness and restoring proper muscle function, individuals often experience enhanced mobility, better posture, and reduced pain levels that persist over time.
The psoas muscle’s connection to the sympathetic nervous system means that release can also promote emotional balance and reduce stress. Many people report feeling more grounded and relaxed, as the muscle’s tension is no longer contributing to heightened stress responses.
Regular maintenance, such as periodic releases and mindful movement practices, helps sustain these benefits. Over time, the body adapts to the newfound freedom of movement, leading to improved physical performance and a reduced risk of recurring injuries.
Additionally, a healthy psoas muscle supports better breathing patterns and spinal alignment, which can enhance overall vitality and energy levels. Investing in long-term psoas health fosters a stronger connection between body and mind, promoting resilience and well-being for years to come.